
The interest payable account is maintained under the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). By contrast to the accrual principle, the cash accounting principle recognizes an event when cash or compensation is received for an event. Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program.
Issued When Market Rate Equals Contract Rate
An advertising agency signs a $6,000, 3-month note payable (a type of loan) with an annual rate of 10% on October 1st. Interest expense, as previously mentioned, is the money a business owes after taking out a loan. Any time you borrow money, whether from an individual, another business, or a bank, you’ll have to repay it with interest. The interest part of your debt is recognized as an interest expense in your business’ income statement.
Notes Payable Issued to Bank
- By the end of the 5th year, the bond premium will be zero andthe company will only owe the Bonds Payable amount of $100,000.
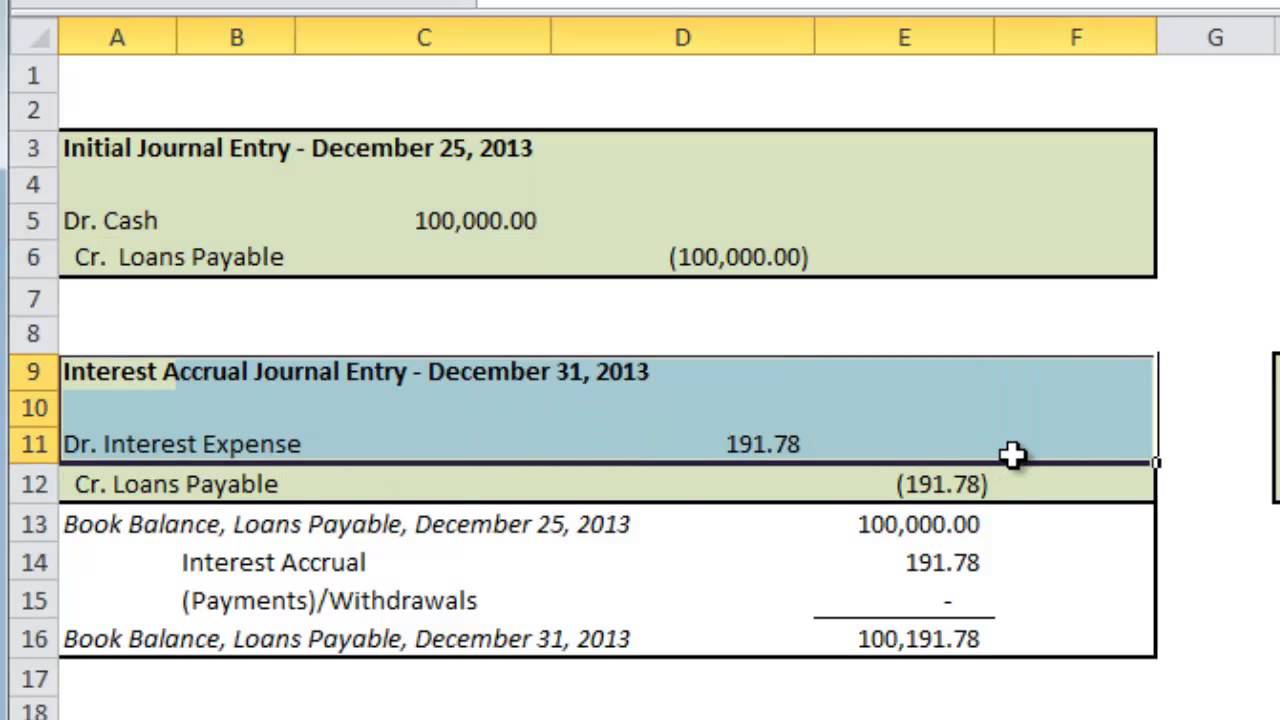
- Interest payable, as the name suggests, accounts for the accumulated interest amount that a firm is yet to pay.
- Until that time, the future obligation might be noted in the notes to the financial statements published in the annual reports.
In addition, it is important to note that the interest payable journal entry must also be recorded in the general ledger. By recording the entries in the general ledger, the company can ensure that all financial information is accurate and up-to-date. The company’s journal entry credits bonds payable for the par value, credits interest payable for the accrued interest, and offsets those by debiting cash for the sum of par, plus accrued interest. The current period’s unpaid interest expense that contributes to the interest payable liability is reported in income statement. Interest is not reported under operating expenses section of income statement because it is a charge for borrowed funds (i.e., a financial expense), not an operating expense.
Interest Payment: Issued When Market Rate Equals Contract
The recording of an unpaid interest amount on the credit side of the journal entry indicates the existence of an obligation to pay. This journal entry is an important at what income does a minor have to file an income tax return tool for businesses to keep track of their interest expenses. The entry is made at the end of the month and includes both the debit and credit side of the ledger.
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Interest Payable is a liability account that reports the amount of interest the company owes as of the balance sheet date. Accountants realize that if a company has a balance in Notes Payable, the company should be reporting some amount in Interest Expense and in Interest Payable. The reason is that each day that the company owes money it is incurring interest expense and an obligation to pay the interest.
ABC has to record the interest expense $ 500 per month based on the money borrowed and the interest rate. And also, the interest expense that needs to be paid after December 31st won’t be considered, as we discussed earlier. Now, since the loan was taken on 1st August 2017, the interest expense that would come in the income statement of the year 2017 would be for five months. If the loan were taken on 1st January, then the interest expense for the year would have been for 12 months.
The amountof the cash payment in this example is calculated by taking theface value of the bond ($100,000) and multiplying it by the statedrate (5%). Since the market rate and the stated rate are different,we need to account for the difference between the amount ofinterest expense and the cash paid to bondholders. The amount ofthe discount amortization is simply the difference between theinterest expense and the cash payment. Since we originally debitedBond Discount when the bonds were issued, we need to credit theaccount each time the interest is paid to bondholders because thecarrying value of the bond has changed.
With the accrual basis of accounting, you record expenses as they occur, not when you pay. Before diving into some business examples on how to make journal entries for interest expenses, let’s first go over some accounting basics you’ll need to know. Read on to learn how to calculate the accrued interest during a period. Then, find out how to set up the journal entry for borrowers and lenders and see examples for both. The journal entry is debiting interest expense and credit interest payable.
