
This value does notinclude the interest cost—the cost of borrowing—related to thedebt. Beyond FASB’s preferred method of interestamortization discussed here, there is another method, thestraight-line method. This method is permitted under US GAAP if theresults produced by its use would not be materially different thanif the effective-interest method were used. IFRS does not permitstraight-line amortization and only allows the effective-interestmethod.
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Interest payable on a loan refers to the periodic interest payments that are required to be made by the borrower to the lender under the terms of the loan agreement. The interest rate is typically stated as a percentage of the outstanding principal balance and is paid over the life of the loan. Interest payments are usually made on a monthly basis, but can also be made on a quarterly or yearly basis, based on the loan agreement. Interest payable, as the name suggests, accounts for the accumulated interest amount that a firm is yet to pay. It is a current liability for any organization, which is committed to pay back the amount owed to lenders. The accumulated interests are quite commonly recorded when one deals with a bond instrument.
What is a note payable?
- After that company will record interest expense into income statement while the other side impacts the interest payable.
- Thus, S. F. Giant receives only $5,000 instead of $5,200, the face value of the note.
- Deskera allows you to automate your recurring invoice payments with just a few clicks.
When you borrow money for a house or car, you will pay interest on that amount. The interest that accrues is the amount you owe, usually at the end of the month, which is included in your loan payment. Accurate and timely accrued interest accounting is important for lenders and for investors who are trying to predict the future liquidity, solvency, and profitability of a company. Accrued interest is usually counted as a current asset, for a lender, or a current liability, for a borrower, since it is expected to be received or paid within one year.
Retirement of Bonds When the Bonds Were Issued at Par
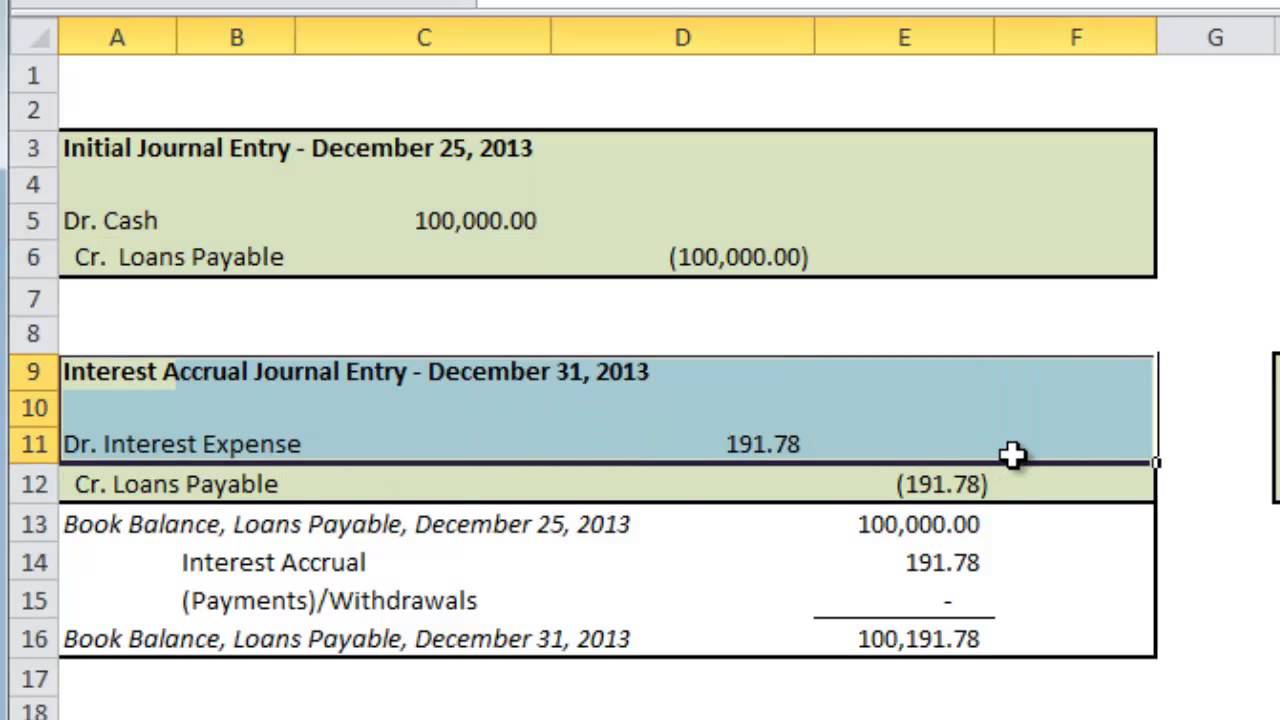
Thus, when these payments are monitored, the firms make sure there is no delayed payment and the amount owed to lenders are paid to avoid any huge increase in the accumulated interest payment figures. Interest payable is a liability that represents the amount of interest owed to creditors but not yet paid. It can be classified as either short-term or long-term, depending on when the interest is due. Short-term interest payable is due within one year, while long-term interest payable is due more than one year from the balance sheet date. Interest payable is typically combined with other current liabilities on the balance sheet, but it may also be presented as a separate line item.
Financial Accounting
A discount on a note payable is the difference between the face value and the discounted value at issuance. This interest expense is allocated over time, which allows for an increased gain from notes that are issued to creditors. Taking out a loan directly from the bank can be done relatively easily, but there are fees for this (and interest rates). Issuing notes payable is not as easy, but it does give the organization some flexibility. For example, if the borrower needs more money than originally intended, they can issue multiple notes payable. This example demonstrates the least complicated method of a bondissuance and retirement at maturity.
Interest payable is a current liability on the balance sheet that reflects the amount of interest a company owes to its creditors. It is usually accrued each month’s end and is an important liability for the company. This journal entry is made to record the cash outflow for the interest payment together with the removal (debit) of the interest payable that the company has recorded in the prior period. The organization borrows money from the owner of the firm, and the borrower agrees to repay the amount borrowed plus interest at a specified date in the future. Generally, there are no special problems to solve when accounting for these notes. At some point, a company will need to record bondretirement, when the company pays the obligation.
The calculator returns the amount of the mortgage payment.Mortgages are long-term liabilities that are used to finance realestate purchases. We tend to think of them as home loans, but theycan also be used for what real estate business expenses are tax deductible commercial real estate purchases. Since the market rate and the stated rate aredifferent, we again need to account for the difference between theamount of interest expense and the cash paid to bondholders.
The interest payments on a loan can have a significant impact on the income statement if the company relies on debt rather than equity. It is important to carefully compare the interest rates offered by different lenders before taking a loan. By understanding the components of interest payable, businesses can ensure that they are accurately accounting for and paying their creditors. Furthermore, businesses can use the information to inform their financial decisions and ensure that they are making wise investments. Interest payable is a critical component of financial management for businesses. It is the amount of interest that a company owes to its creditors for a period of time.
For example, XYZ Company issued 12% bonds on January 1, 2017 for $860,652 with a maturity value of $800,000. The yield is 10%, the bond matures on January 1, 2022, and interest is paid on January 1 of each year. At the end of 5 years, the company will retire the bonds bypaying the amount owed.
Unless the interest is paid up to date, the company will always owe some interest to the lender. A business owes $1,000,000 to a lender at a 6% interest rate, and pays interest to the lender every quarter. After one month, the company accrues interest expense of $5,000, which is a debit to the interest expense account and a credit to the interest payable account. After the second month, the company records the same entry, bringing the interest payable account balance to $10,000. After the third month, the company again records this entry, bringing the total balance in the interest payable account to $15,000. It then pays the interest, which brings the balance in the interest payable account to zero.
